
Human Cell Diagram, Parts, Pictures, Structure and Functions Diseases Pictures
Key points. Cells are the smallest unit of life and the building blocks for all organisms. Each component of a cell has its own function. Animal and plant cells differ and they have similarities.
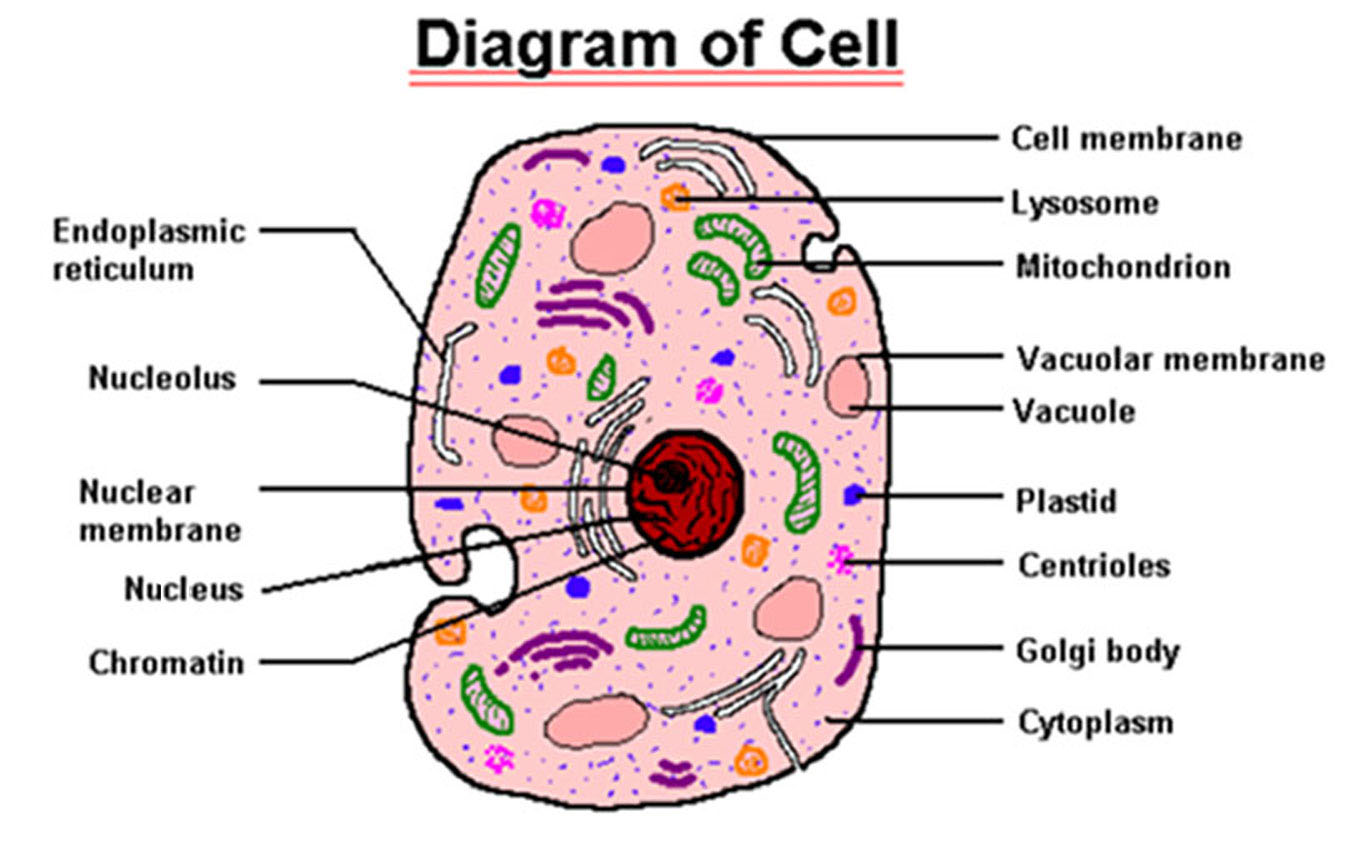
Education 645 High School Biology
Summary. Description. Simple diagram of animal cell (en).svg. English: A simple diagram of an unspecialised animal cell, labelled in English. It shows the cell membrane, nucleus and mitochondria. Due to rendering issues, text has been converted to paths, check bottom layer for editable text. (Font is Zona Pro)
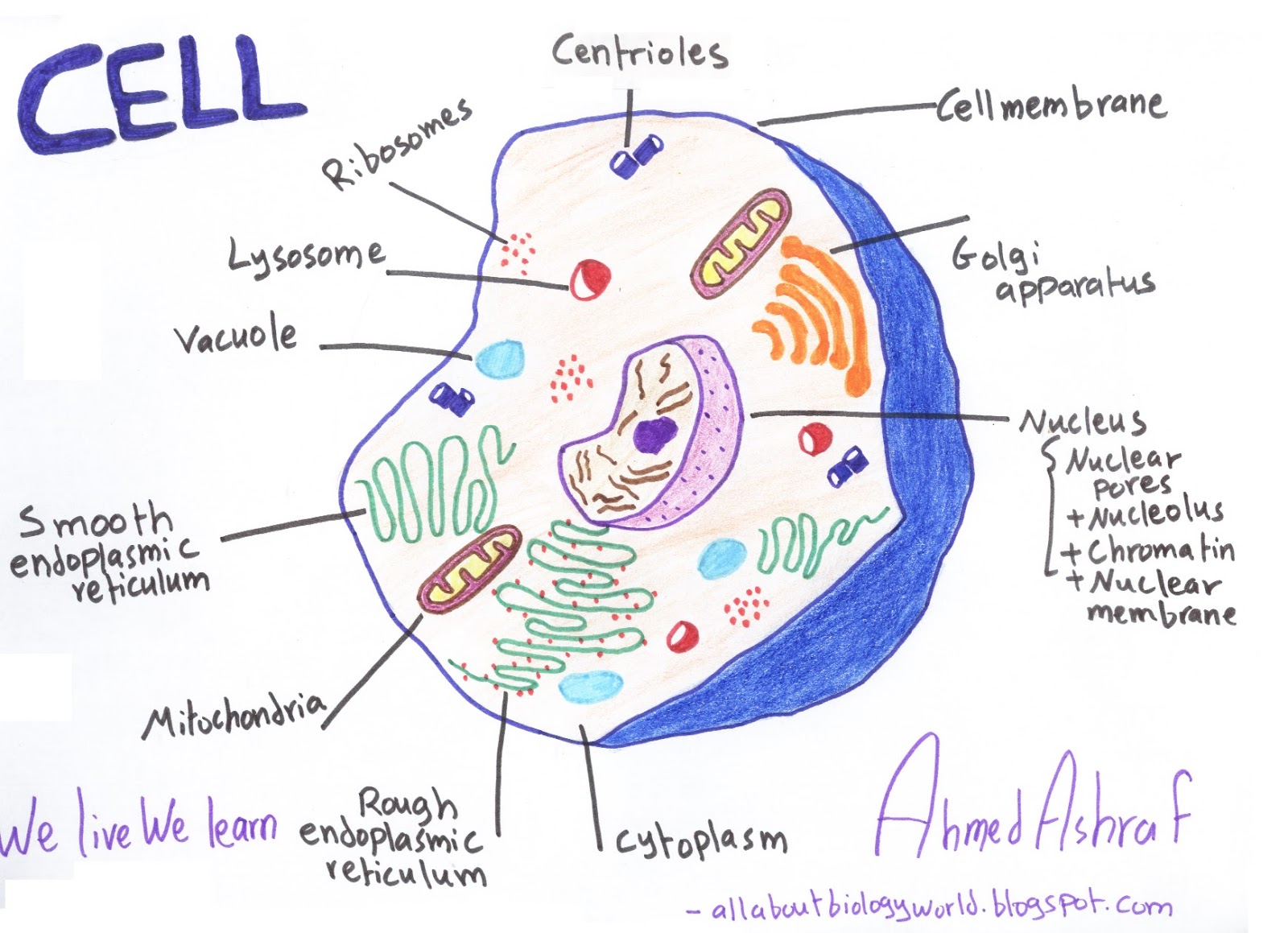
Biology Club Our cells 1 ( structure, function, division, disorder & cycle )
A simple cell in the primary visual cortex is a cell that responds primarily to oriented edges and gratings. However, it has been claimed that the Gabor model does not conform to the anatomical structure of the visual system as it short-cuts the LGN and uses the 2D image as it is projected on the retina.

The animal cell diagram. Vector illustration on white Etsy in 2021 Animal cell, Cell diagram
Cell Definition "A cell is defined as the smallest, basic unit of life that is responsible for all of life's processes." Cells are the structural, functional, and biological units of all living beings. A cell can replicate itself independently. Hence, they are known as the building blocks of life .

Human cell diagram Etsy in 2021 Human cell diagram, Cell diagram, Human cell structure
What are cells? The ultrastructure of cells Structure of fungal and bacterial cells The functions of cell organelles What are cells? Cells are the building blocks of all living.

Overview of Cell Structure
GCSE AQA Trilogy Cell structure - AQA Animal cells Organisms are made up of cells. Most organisms are multicellular and have cells that are specialised to do a particular job. Microscopes.

Animal Cell Diagram Simple Get More Anythink's
Animal cell size and shape. Animal cells come in all kinds of shapes and sizes, with their size ranging from a few millimeters to micrometers. The largest animal cell is the ostrich egg which has a 5-inch diameter, weighing about 1.2-1.4 kg and the smallest animal cells are neurons of about 100 microns in diameter.
.svg/1280px-Simple_diagram_of_plant_cell_(en).svg.png)
FileSimple diagram of plant cell (en).svg Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
cell, in biology, the basic membrane-bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed. A single cell is often a complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium or yeast. Other cells acquire specialized functions as they mature. These cells cooperate with other specialized cells and become.
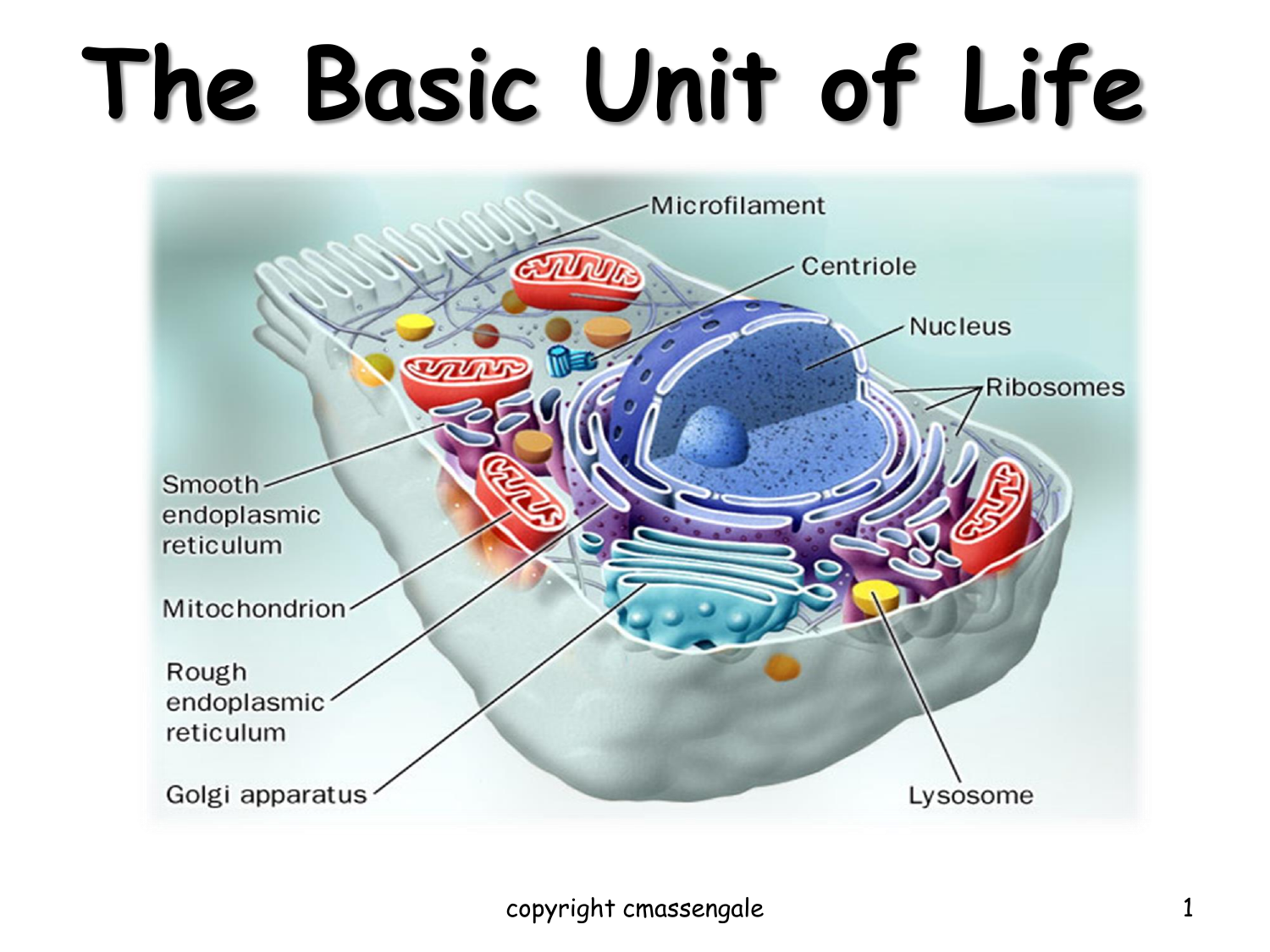
Cell Anatomy Interactive For Kids Cell Cell Structure Biology Gambaran
To distinguish individual cells in a piece of tissue or individual bacteria in a sample of liquid required the development of relatively high-powered microscopes, instruments used for magnifying objects otherwise too small to be seen. For more on how microscopes are used in biology today, check out the article on microscopy.

What is a cell? Facts
Structure of a cell: Unit test; About this unit. This unit is part of the Biology library. Browse videos, articles, and exercises by topic.. Basic characteristics of the cell Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Quiz 1. Level up on the above skills and collect up to 240 Mastery points Start quiz.
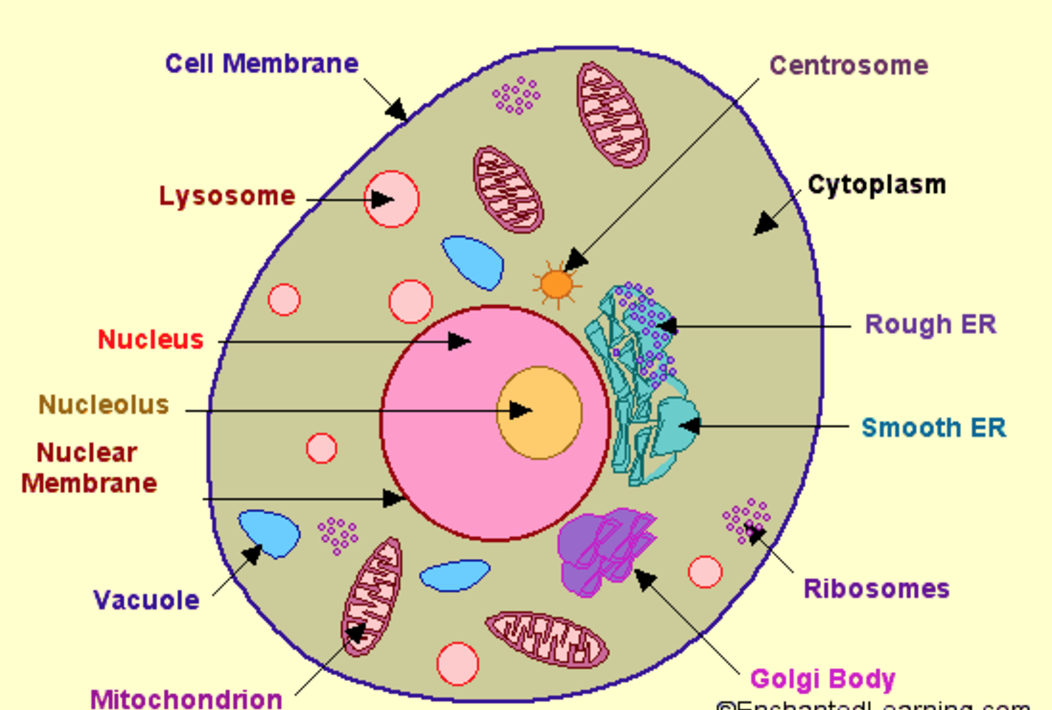
Structure of cell Cell structure and functions, Class 8
Definition. Animal cells are the basic unit of life in organisms of the kingdom Animalia. They are eukaryotic cells, meaning that they have a true nucleus and specialized structures called organelles that carry out different functions. Animal cells do not have plant-specific organelles like cell walls, which support the plant cell, or.

animal cell diagram easy Kris Hammett
Introduction to the cell. Cells are the most basic unit of life. All cells have a membrane that separates them from the outside world. Although cells are small, they are not simple. Cells contain different components, such as the cytoplasm, ribosomes, and genetic information in the form of DNA.

Cell Structure
Key points: All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out. The cell membrane surrounds a cell's cytoplasm, which is a jelly-like substance containing the cell's parts. Cells contain parts called organelles. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell.

Cells Mr. Scott's 6th Grade Class
Every cell is different but there is a basic structure that is common to all cells. A cell is essentially genetic material in a gel-like substance surrounded by a membrane. The genetic material of cells is found as molecules called DNA. The DNA of a cell holds all the information that a cell needs to keep itself alive.
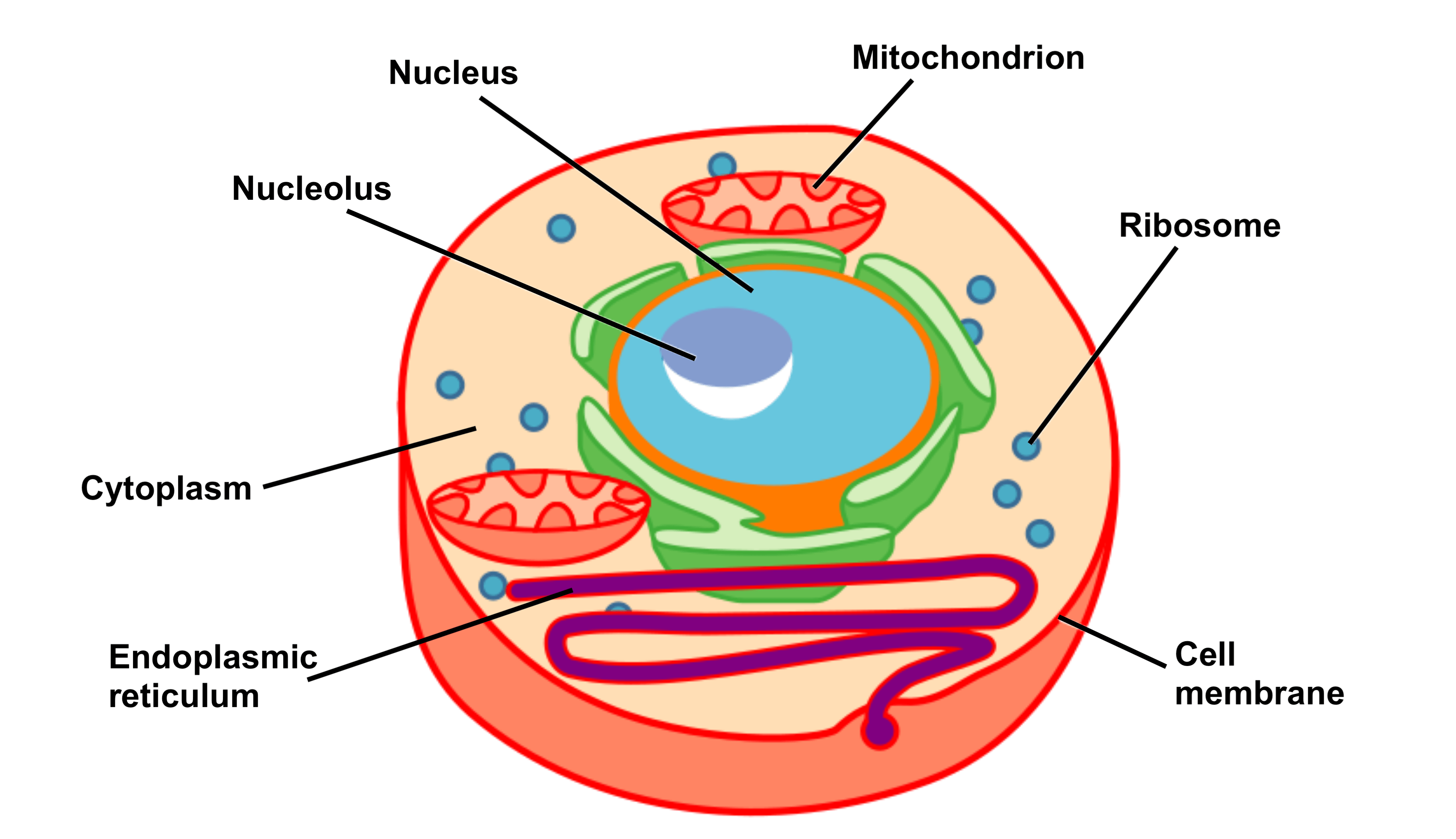
Cell Structure and Function Part 1 The Organelles Medical Exam Prep
Cell diagram labeled Cell diagram unlabeled Learn faster with interactive cell quizzes Sources + Show all What are the parts of a cell? There exist two general classes of cells: Prokaryotic cells: Simple, self-sustaining cells (bacteria and archaea) Eukaryotic cells: Complex, non self-sustaining cells (found in animals, plants, algae and fungi)
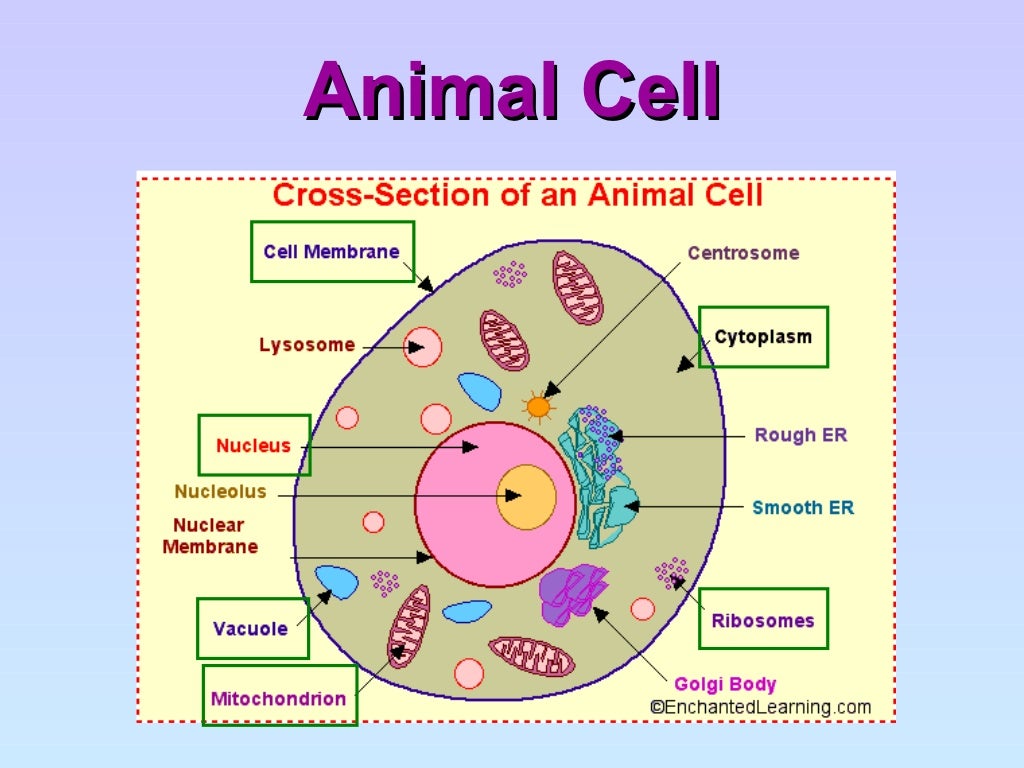
Animal Cell Structure Basic / Cell Structure Cells Structure and characteristics of an
All eukaryotic cells consist of three basic parts. These are the cell membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm. The cell membrane surrounds the outside of the cell, the nucleus is found in the middle of the cell, and the cytoplasm fills the gap between the two. Buried in the cytoplasm are hundreds or thousands of subcellular structures called.